Abstract
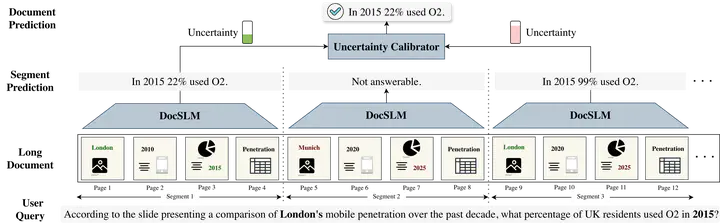
Large Vision–Language Models (LVLMs) have demonstrated strong multimodal reasoning capabilities on long and complex documents. However, their high memory footprint makes them impractical for deployment on resource-constrained edge devices. We present DocSLM, an efficient Small Vision–Language Model designed for long document understanding under constrained memory resources. DocSLM~ incorporates a Hierarchical Multimodal Compressor that jointly encodes visual, textual, and layout information from each page into a fixed-length sequence, greatly reducing memory consumption while preserving both local and global semantics. To enable scalable processing over arbitrarily long inputs, we further introduce a Streaming Abstention mechanism that operates on document segments sequentially and filters low-confidence responses through an entropy-based uncertainty calibrator. Across multiple long multimodal document benchmarks, DocSLM~matches or surpasses state-of-the-art methods while using 82% fewer visual tokens, 75% fewer parameters, and 71% lower latency—delivering reliable multimodal document understanding on lightweight edge devices. Code and Model are available in https URL.